“Our decade of experience in the analytical sciences is what sets Elevate Scientific apart . . . “
Dr. Robert Turner, Chief Scientist and CEO, Elevate Scientific
Cannabinoid Potency
General Summary:
The active components present in cannabis flower and manufactured medical marijuana products are quantified to assess quality. The state requires all harvest and production batches be tested for total THC. Other active cannabinoids are analyzed such as CBDA, CBD, CBGA, CBG, THCV, CBDV, CBC, including their degradation products, d8-THC and CBN. These can be useful for assessing product age and storage conditions.
Technology: HPLC (High-Performance Liquid Chromatography) from Thermo Scientific with PDA detector


Heavy Metals
General Summary:
Heavy metals are present in soils, water, nutrients, and pesticides. Cannabis plants naturally accrue heavy metals through uptake in their root system. Most heavy metals are safe in small doses, but high levels of exposure or consumption can lead to heavy metal poisoning.
Technology: Inductively coupled plasma / mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) – Perkin Elmer
Legal Limits:
| Mercury < 0.1 PPM | Lead < 0.5 PPM | Arsenic < 0.2 PPM | Cadmium < 0.2 PPM |
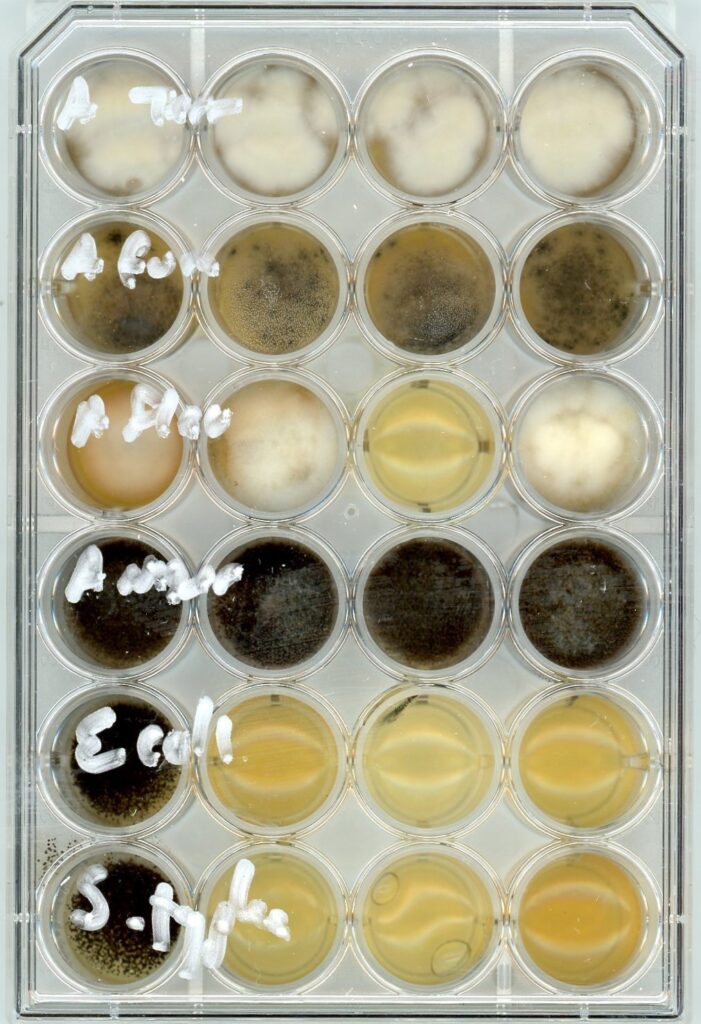
Microbiology
Technology:
Culture and microscopic inspection
Description:
Our samples are screened for Total Yeast and Mold, Aspergillus niger, A. flavus, A. terreus, A. fumigatus, Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli (STEC), and Salmonella spp. Aspergillus spp. are known to pose risks to the respiratory pathways and certain molds produce aflatoxins. Yeast contamination in the body can lead to autointoxication syndrome. E. coli (STEC) and Salmonella can disrupt the functions of the digestive system and produce harmful toxins inside the body.

Pesticides
Technology:
Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS)
Description:
Pesticides are a family of compounds including herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. Pesticides bioaccumulate in the upper levels of the food chain and can cause significant health problems to people and native wildlife. The analysis is done using a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer with an electrospray ionization source
Mycotoxins
Technology:
Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS)
Description:
Mycotoxins are produced by fungi as a form of biological warfare to remove competition for resources and predation. These compounds can be airborne and can cause neurological and physiological diseases when significant concentrations arise from a mold bloom. The analysis is done using a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer with an electrospray ionization source


Terpenes
General Summary:
Terpenes are aromatic compounds found in cannabis. This bouquet of smells determines the full range of the cannabis flowers flavor profile. The state of Oklahoma defines a flowers potency by its cannabinoid and terpinoid profiles.
Technology: GC MS (Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry)
| Terpene | Aroma | Terpene | Aroma |
| alpha-Bisabolol | citric and floral | D-Limonene | orange, citrus smell |
| Camphene | Essential oils | Linalool | flowers |
| delta-3-Carene | sweet, pine, cedar, woodsy, and pungent | beta-Myrcene | clove, earthy |
| -)-Caryophyllene Oxide | lemon balm | cis-Nerolidol | citrus |
| beta-Caryophyllene | woody, black-peppery | trans-Nerolidol | citrus |
| p-Cymene | musty orange | Ocimene | floral |
| Eucalyptol | minty | Alpha-Pinene | pine |
| Geraniol | floral, fruity | beta-Pinene | pine |
| Guaiol | wood and smoke | alpha-Terpinene | sour citrus |
| Humulene | hops | gamma Terpinene | Sweet citrus |
| Isopulegol | mint | Terpinolene | smokey or woody |
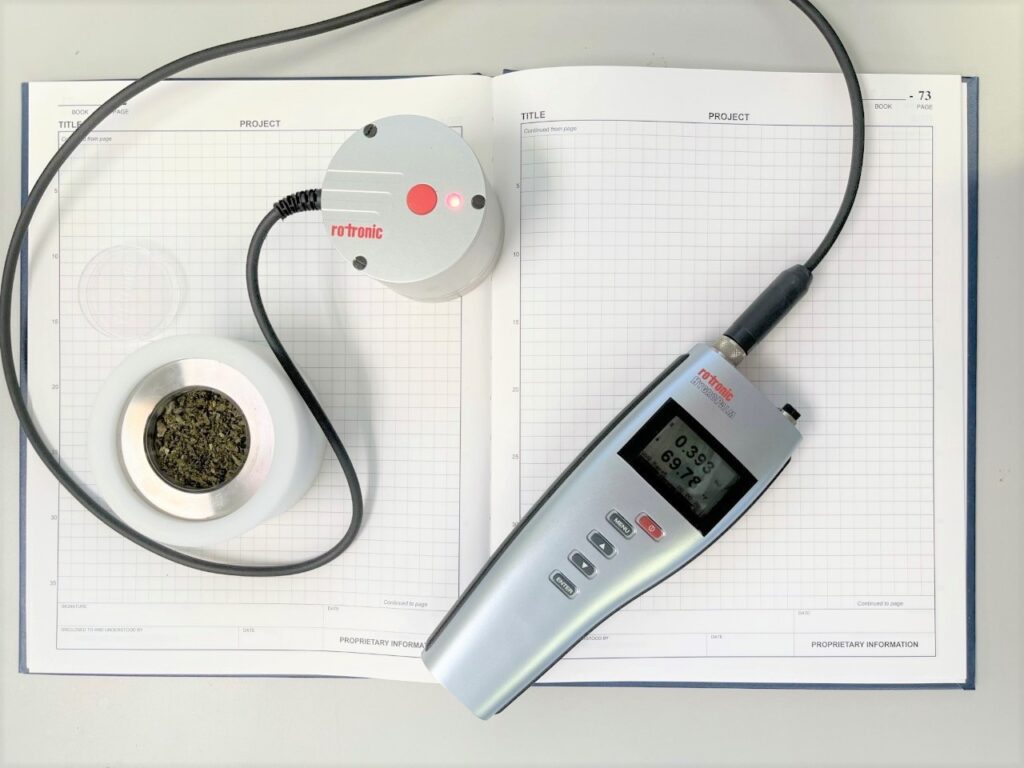
Water Activity
General Summary:
Water activity measures the level of water bound to the surface of a product. This test is used to determine the stability and shelf life of cannabis flower. The higher the water activity, the higher the likelihood microbial growth could occur down the line. High levels of water activity can also have an impact on the breakdown of THC.
Technology:
Water activity meter
Legal Limits:
< 0.65 A.W.
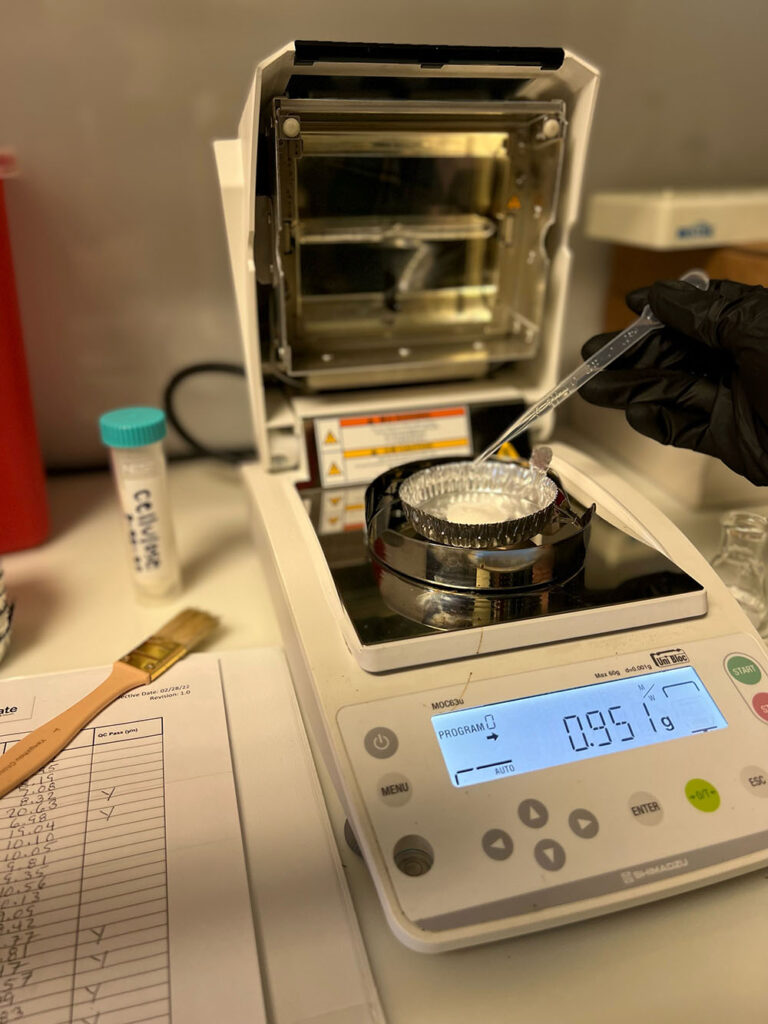

Moisture Content
General Summary:
Cannabis has naturally occurring moisture within the flower. The primary purpose of testing for moisture content is to determine the efficacy of how the flower was dried and cured. If the sample has excess moisture it can create the ideal environment for mold and bacteria to grow. Additionally, moisture content allows us to determine the dry weight of the sample by removing the percent of moisture present into the equation.
Technology:
Moisture balance analyzer
Legal Limits:
< 15.0%
Residual Solvents
General Summary:
The process for the manufacturing of distillate can involve many different types of organic solvents. For this reason, the state requires that all manufactured products be tested for 11 different organic solvents. This helps to ensure the safety of all patients.
Technology: HS GC MS (Headspace Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry) from Thermo
Legal Limits:
| Acetone <1,000 ppm | Benzene <1,000 ppm | Butane <1,000 ppm | *Ethanol <5,000 ppm |
| Heptane <1,000 ppm | Hexane <60 ppm | Isopropanol <1,000 ppm | Pentane <1,000 ppm |
| Propane <1,000 ppm | Toluene <180 ppm | Xylenes <430 ppm |
